
There is a clear evidence of an underlying atrial muscle disease in patients with the WPW syndrome. However, since AF still occurs in some patients with the WPW syndrome even after successful ablation of the AP, there should be other mechanisms responsible for the development of AF in the WPW syndrome. Several studies demonstrated a decrease incidence of AF after successful elimination of the AP, suggesting that the AP itself may play an important role in the initiation of AF. AF can also be initiated by ectopic beats originating from the pulmonary veins, and elsewhere. Focal activity, multiple reentrant wavelets, and macroreentry have all been implicated in AF, perhaps under the further influence of the autonomic nervous system. There are several possible mechanisms that may be involved in the development of AF in the WPW syndrome, namely, spontaneous degeneration of atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia into AF, the electrophysiological properties of the AP, the effects of AP on atrial architecture, and intrinsic atrial muscle vulnerability. As to potential reasons for why AFib may be more common in patients with WPW - I found a number of potential causes/contributing factors suggested in this 2011 article by Centurion ( ) - who says, “it is very important to know the mechanisms involved in the development of AF in the WPW syndrome.

Thanks for your EXCELLENT question Patrick. ( CLICK HERE - for more on risk assessment of the patient with WPW). Given this high risk of developing a potentially lethal WPW-associated arrhythmia - the young adult patient in this case would be best advised to strongly consider undergoing catheter ablation of his AP. This corresponds to a shortest R-R interval that is barely more than one large box in duration - which is essentially what we see for the R-R intervals between beats #5-6 10-11 20-21 26-27 and 30-31 in ECG #1.

The risk of developing VFib during AFib in a patient with WPW is greatly increased when the SPERRI ( Shortest Pre- Excited R- R Interval ) measures below 220-250 msec. PEARL #4: Not all patients with WPW are at risk of developing potentially life-threatening tachyarrhythmias.CLICK HERE and HERE - for more on the ECG diagnosis of arrhythmias in patients with WPW.
This is another “soft” clue that the rhythm is not VT, in which the patient is likely to be more symptomatic.

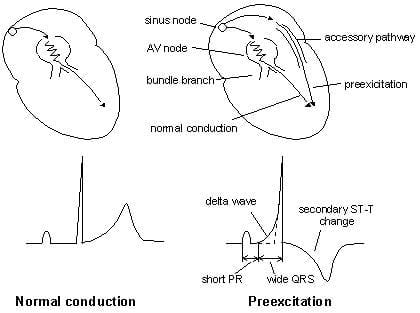
PEARL #2: In addition to an excessively rapid ventricular response - another characteristic ECG finding of AFib in a patient with WPW is a surprisingly large variation in R-R intervals, in which some of the longer R-R intervals are more than twice as long as the shortest R-R intervals (ie, as occurs for the R-R intervals between beats #7-8 and 21-22).PEARL #1: Recognition that AFib with a wide QRS complex attains a ventricular response that at times exceeds 220/minute - instantly tells you that the patient must have WPW ( Wolff- Parkinson- White ) Syndrome, in which AFib impulses are by-passing the AV node, and are being conducted to the ventricles over an AP ( Accessory Pathway).A ventricular response that at times attains a rate of ~220-250/minute is simply too fast for atrial impulses to be transmitted over the normal ( AV nodal ) conduction pathway. Under normal conditions with AFib - the refractory period of the AV node does not allow more than 150-to-200 impulses/minute to be conducted to the ventricles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
